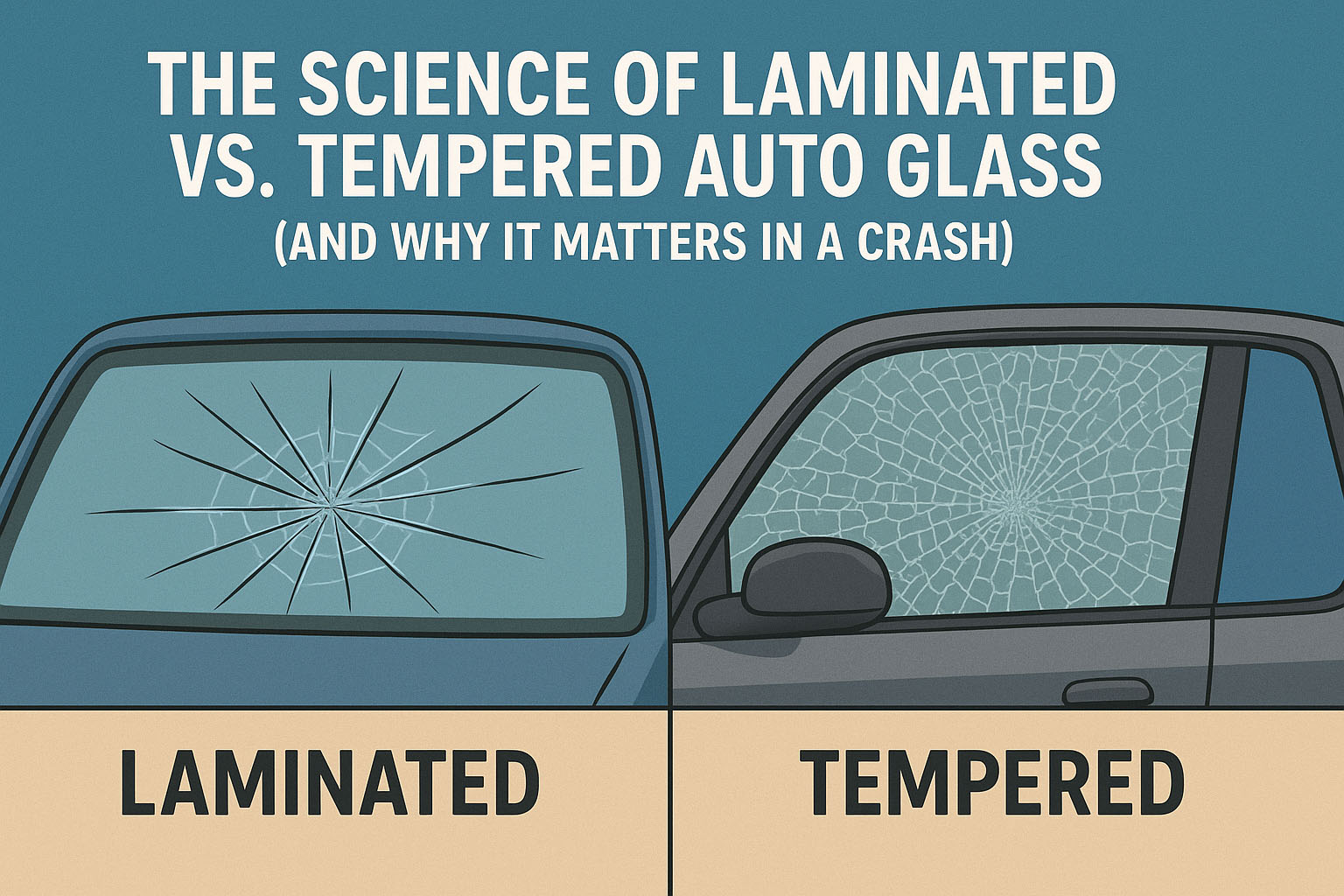
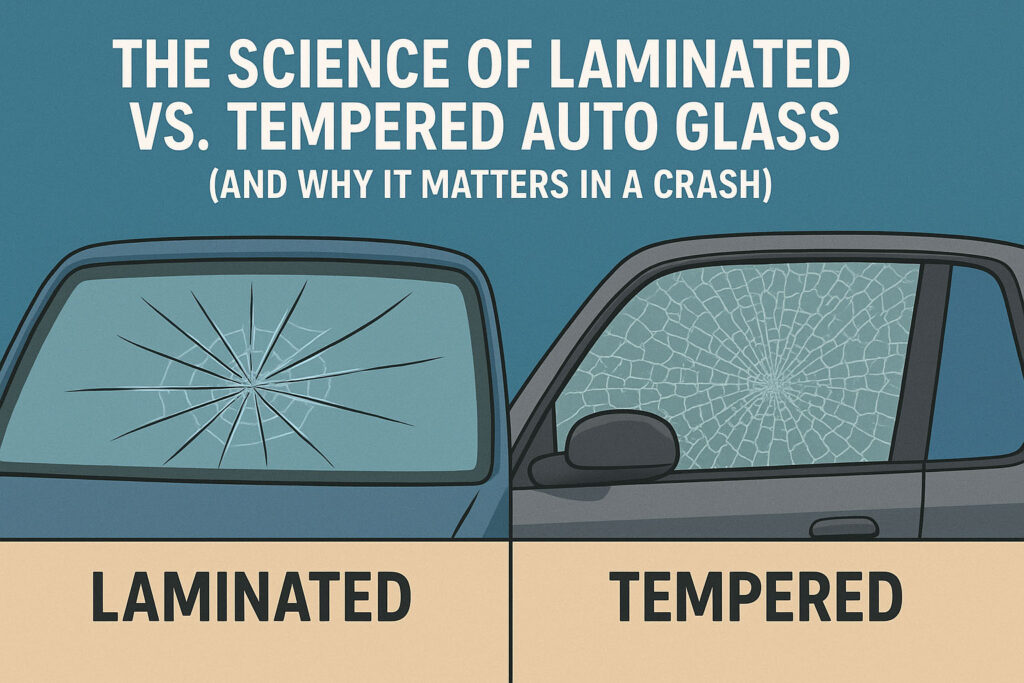
When it comes to vehicle safety, your windshield and windows play a far bigger role than just keeping out wind and rain. Modern auto glass is engineered to protect you during an accident, using two primary types of glass: laminated and tempered. Each has a unique design and purpose, and understanding the science behind them can help you appreciate why they’re critical for your safety.
Laminated Glass: Built for Impact Resistance
Laminated glass is most commonly used in windshields. It’s made by bonding two layers of glass with a thin, durable layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or a similar resin in between. This layered structure offers several advantages:
- Shatter Resistance: In a collision, laminated glass may crack, but it usually stays in one piece thanks to the inner plastic layer. This prevents sharp shards from flying into the cabin.
- Structural Integrity: The windshield provides up to 30% of a vehicle’s structural strength in a rollover. Laminated glass helps keep the roof from collapsing.
- Occupant Protection: If airbags deploy, the windshield acts as a backstop, ensuring the airbags cushion you effectively.
- Security: Laminated glass is harder to break through, offering added protection against theft.
Essentially, laminated glass is designed to hold together under stress, keeping drivers and passengers safer during a crash.
Tempered Glass: Designed to Crumble Safely
Tempered glass is most often used in side and rear windows. Unlike laminated glass, it’s manufactured through a process of rapid heating and cooling that strengthens the glass significantly. Its benefits include:
- Strength: Tempered glass is roughly four to five times stronger than regular glass of the same thickness.
- Shatter Pattern: When it breaks, it crumbles into small, rounded pebbles instead of sharp, jagged shards. This reduces the risk of severe cuts.
- Emergency Exit: Because it breaks into smaller pieces, tempered glass allows occupants (or rescuers) to quickly remove the window in an emergency situation.
Tempered glass is ideal for areas where quick exit or rescue is essential, while still providing durability under normal conditions.
Why the Difference Matters in a Crash
In an accident, the type of auto glass can directly affect your chances of injury or survival:
- Windshields (laminated) help keep you inside the vehicle, reduce head injuries, and provide structural support.
- Side/Rear Windows (tempered) allow for quick escape routes and minimize deep lacerations if shattered.
- Combination Safety: Together, laminated and tempered glass create a system that balances strength, containment, and accessibility.
Newer vehicles are also beginning to use laminated side windows, especially in luxury models, to further improve crash protection and reduce noise inside the cabin.
A Note on Replacement and Safety
Not all glass is created equal, and when you replace your windshield or windows, it’s important to use OEM-quality auto glass. Low-quality replacements may lack the proper laminating materials or tempering strength, reducing safety in an accident.
If your windshield is damaged, don’t wait to repair or replace it. Even small cracks can compromise the laminated structure and reduce its ability to protect you in a crash.
Key Takeaway
The science of auto glass is more than just materials — it’s about saving lives. Laminated glass holds strong during collisions, while tempered glass breaks safely to protect and free passengers. Together, they form a crucial part of your vehicle’s safety system.
If you need a windshield or window replacement, use Glass.net’s free tool to compare quotes from trusted local shops and ensure your vehicle’s safety glass is replaced with the right materials.
To read more, visit blog.glass.net